Prerna Sahni
Dec 22, 2025
Agentic AI
Agentic AI vs Generative AI: How They Work & Why They Matter
Artificial intelligence has entered a new era. While generative AI took the world by storm in 2023–2024, generating human-like content at an unprecedented scale, a new paradigm is now emerging in which Agentic AI systems can autonomously plan, reason, and execute end-to-end tasks.
Understanding the difference between agentic AI and generative AI is no longer optional for tech leaders, engineers, and decision-makers. As we move deeper into 2025, these two AI waves are merging, reshaping enterprise workflows, developer ecosystems, and digital automation at lightning speed.
This blog will demystify how they work, where they differ, and what the explosive rise of AI agent systems, Autonomous AI agents, and AI automation tools means for the future of intelligent technologies.
1. Introduction
Artificial intelligence is entering a defining moment. In 2023–2024, when the world of writing, coding, designing, and communicating exploded with Generative AI, the industry is now experiencing a powerful new shift, the rise of Agentic AI. Unlike traditional generative models that wait for prompts to generate text, agents of agentic systems can plan, reason, use tools and execute a task on their own. AI is evolving from a tool to a partner in this transformation.
As we approach the end of 2025, it is crucial for engineers, decision-makers, and organizations to understand the difference between these two paradigms. Companies such as MLAI DIGITAL are leading the charge in this development of agentic systems that advance automation, intelligence, and real-world impact.
2. Generative AI: What It Is and How It Works
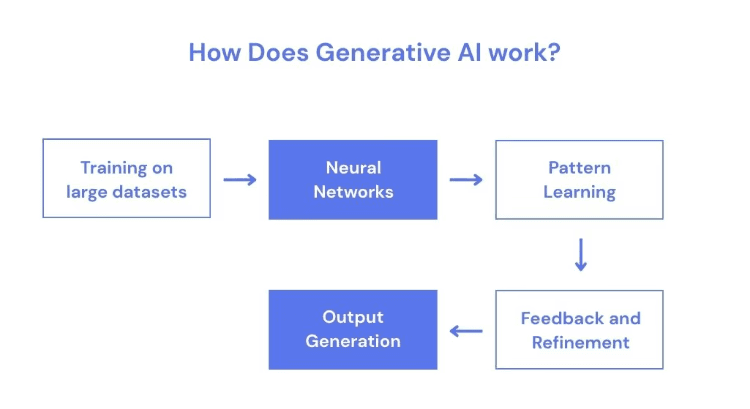
Generative AI refers to models that are made to produce new content like text, images, code audio, videos, and synthetic data. These systems function according to a very simple principle: you supply a prompt, and the model delivers an output. They rely heavily on learned patterns from their training data and follow a straightforward flow where the input is processed; the next most likely token or pixel is predicted, and the output is produced.
Generative AI is based on transformers like Claude, Gemini and GPT, diffusion models like Stable Diffusion, and multimodal system like Gemini and GPT-Vision. These models work by seeing your input and predicting the most suitable continuation. This is the reason owing to which some tools like ChatGPT can write articles or code, Midjourney can create hyper-realistic images, and Gemini can translate documents and generate multimedia content.
Generative AI excels at:
Producing high-quality content
Recalling structured information
Supporting creativity and brainstorming
Having natural conversations and answering queries
However, it also comes with limitations that prevent it from operating independently.
Some key drawbacks of generative AI include:
No autonomy to start or continue tasks on its own
No long-term planning or reasoning loops
No learning from new experiences beyond its training data
No ability to act in the real world or use external tools unless prompted
Generative AI is powerful, but it remains fundamentally passive. It responds, but it does not act. This gap is what agentic AI is designed to fill.
3. Agentic AI: What It Is and How It Works
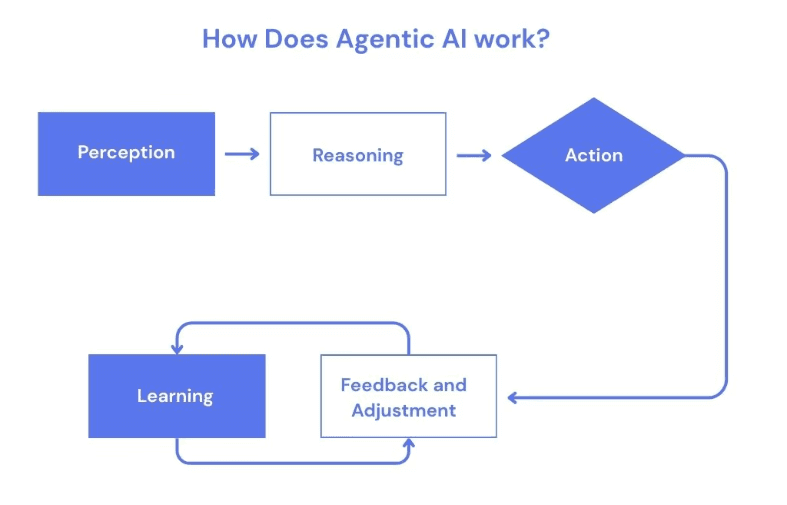
Agentic AI is the next major evolution in artificial intelligence. Instead of only generating information, agentic systems can act, plan, decide, use tools, and learn from their own actions. They work more like independent digital workers than digital assistants waiting for instructions. An agent doesn't simply respond to something; it works toward a goal.
At the heart of agentic AI is a dynamic cycle:
Sense the environment
Think and create a plan
Act to execute tasks
Learn and improve through feedback
Agentic AI incorporates several key capabilities:
Autonomy to make decisions without constant human input
Reasoning loops that allow multi-step thought, verification, and refinement
Tool usage, enabling interaction with APIs, browsers, apps, and databases
Planning modules that break down complex goals into smaller tasks
Self-evaluation systems that review outputs for errors or hallucinations
Under the hood, agentic AI includes memory systems, planning engines, reasoning modules, tool-calling frameworks, and execution layers. This allows it to handle continuous operations, multi-step workflows, enterprise integrations, and real-time adaptability things generative AI alone cannot achieve.
Examples of agentic AI in action include:
AutoGPT, one of the first autonomous task executors
Devin, the AI software engineer capable of writing and debugging code
CrewAI, which coordinates multiple agents working together
BabyAGI-like frameworks, used for research, planning, and long-running tasks
Agentic AI transforms artificial intelligence from a passive creator into an active problem-solver capable of independent, goal-driven behavior. It represents the shift from “generate on request” to “act intelligently,” paving the way for the next era of AI systems.
4. Key Differences: Agentic AI vs. Generative AI
Feature | Generative AI | Agentic AI |
Autonomy | Reactive, requires prompts | Proactive, executes autonomously |
Decision-making | Limited | Advanced, multi-layered |
Reasoning depth | Shallow–moderate | Deep reasoning and verification loops |
Learning capabilities | Static post-training | Dynamic through memory and feedback |
Task execution | Single-step outputs | Multi-step end-to-end workflows |
Memory structure | Limited session memory | Robust multi-tier memory |
Real-world applications | Content and ideation | Automation and operations |
Limitations | Hallucination, no autonomy | Over-autonomy risks, safety concerns |
In essence, generative AI creates, while agentic AI accomplishes.
5. Real-World Use Cases
5.1 Generative AI Use Cases
(a) Content creation – blogs, emails, ads, documentation
Generative AI can output polished written content quickly and at scale, making it the perfect tool for marketing teams, writers, and businesses. It saves time with writing and keeps the tone and style consistent throughout.
(b) Synthetic data generation – training datasets, simulations
It creates realistic but artificial datasets that help train models when real data is limited or sensitive. It has immense value in fields like health and finance.
(c) Customer support – automated chats, responses
Generative AI powers chatbots that can answer common questions and handle basic customer queries. This reduces support workload while offering faster responses.
(d) Ideation and drafting – brainstorming, mockups, outlines
It helps users with the creative process by proposing ideas, structuring outlines, and drafting text. This makes ideation of projects in the early stage faster.
(e) Code generation – boilerplate, components, debugging
Generative AI can write repetitive code, create components and spot bugs. It speeds up development and cuts down on manual coder effort.
5.2 Agentic AI Use Cases
(a) Autonomous coding – writing, testing, deploying projects end-to-end
An agentic AI can take on a coding task, break it down into steps, write the code, test it, debug and deploy the final output. It makes it a great deal more like a digital software engineer than project coder.
(b) Workflow automation – handling multi-system processes
It easily integrates with various tools and platforms to complete multi-step processes across apps. IT teams, operations, and enterprises who manage complex workflows will find this useful.
(c) Research agents – scanning web, summarizing findings, citing sources
Agentic AI can autonomously browse information, verify sources, and produce structured summaries. It reduces hours of manual research into minutes.
(d) Business process automation – HR, finance, marketing operations
Companies use agentic AI for tasks like processing forms, updating CRM systems, managing approvals, and making routine decisions. It acts like an additional operations team member.
(e) Real-time task execution – scheduling, monitoring, decision-making
Agentic AI analyzes live data, discovers issues as they arise, and acts without human intervention. This is valuable in areas like cybersecurity, logistics, and smart operations.
6. Why Agentic AI Matters (And Why It’s Growing Fast)
Agentic AI solves the biggest limitations of generative AI by enabling:
Iteration: refining outputs through repeated improvement
Planning: breaking complex objectives into structured steps
Tool use: interacting with external software and real-world systems
Memory: storing knowledge across sessions
Feedback loops: learning from mistakes and adjusting strategies
For enterprises, this means enormous benefits:
Reduced operational workload
Intelligent automation at scale
Increased productivity and efficiency
Reliable execution with fewer human interventions
Enhanced decision-making accuracy
The rise of AI automation tools, AI agent systems, and autonomous decision-making systems is transforming how companies build products and deliver services.
7. Challenges and Risks
7.1 Generative AI Risks
(a) Hallucination: generating incorrect information
Sometimes, generative AI creates answers that sound right but aren’t really correct. It predicts patterns, instead of confirming the truth. This is why this happens.
(b) Bias: reflecting biases from training data
If the data which is used for training is biased socially, culturally, or historically, then there are chances that AI will not be able to avoid it and instead reproduce those biases. This can lead to unfair or skewed outputs.
(c) Misinformation: producing plausible but false content
Generative AI creates text or pictures that look so genuine that important matters could be misconstrued if not reversed by humans.
7.2 Agentic AI Risks
(a) Over-autonomy: performing unintended actions
An overly independent agent may take actions beyond what the user intended. This becomes risky when the agent interacts with tools, systems, or external applications.
(b) Execution errors: mistakes during automated operations
Because agentic AI performs multi-step tasks, one incorrect decision can lead to cascading errors. This is especially concerning in coding, finance, or enterprise workflows.
(c) Alignment issues: ensuring agent behavior remains controlled
It is quite hard for the agent’s goals to align with that of the user. Without right guardrails, the agent could optimize the wrong thing or misinterpret the instructions.
(d) Data exposure risks: improper handling of sensitive information
When Agentic AI connects to external tools or databases, it can cause sensitive data to leak or become misused or exposed when not properly configured.
8. The Future: Where Agentic AI and Generative AI Are Headed
The future is not one or the other; it is hybrid systems combining the strengths of both.
Expect:
Agentic + Generative fusion models where LLMs act as the intelligence core powering agents
Self-improving agents capable of continuous learning
End-to-end automated workplaces where agents operate entire departments
Transformations in software engineering, product development, and RPA ecosystems
Massive growth in multi-agent systems enabling collaborative task execution
Between 2025 and 2030, AI will shift from being a “smart assistant” to becoming an autonomous collaborator.
Summary
Agentic AI and Generative AI are changing the landscape of intelligent technologies. Generative models such as ChatGPT and Gemini have the ability to create text, code, and media yet remain reactive. Agentic AI can carry out multi-step tasks all on its own. It does so through planning, reasoning, and using a range of tools to get the job done. This guide explains how these two paradigms differ, why agentic systems are rapidly rising in 2025, and how they’re transforming automation, engineering, and enterprise operations. As hybrid AI models become the new standard, companies like MLAI DIGITAL are leading the shift by building advanced agentic systems that deliver true end-to-end automation and intelligent decision-making.


