Prerna Sahni
Jan 3, 2026
LLM
Training LLM Models: Books vs Web Data in 2026
1. Introduction
If you’ve spent any time around AI in the past few years, you’ve probably heard the term LLM models thrown around everywhere. From chatbots to search assistants to enterprise automation platforms, LLM models power almost everything that feels “intelligent” today. But while their capabilities are impressive, their performance still depends on one crucial element: LLM training data.
And in 2026, the core debate around AI training has intensified. Should we train LLM models more heavily on books or on web data? This isn’t just a philosophical argument; it directly shapes accuracy, reasoning, creativity, safety, and real-world applicability.
Books bring depth, long-form reasoning, structure, and clarity. Web data brings recency, diversity, conversational patterns, and practical examples. The performance of LLM models depends on both training and architecture, but the impact depends on the purpose of the model.
So, what is the final verdict? It is not as simple as that, and that is what this blog explores.
2. How LLM Models Learn?
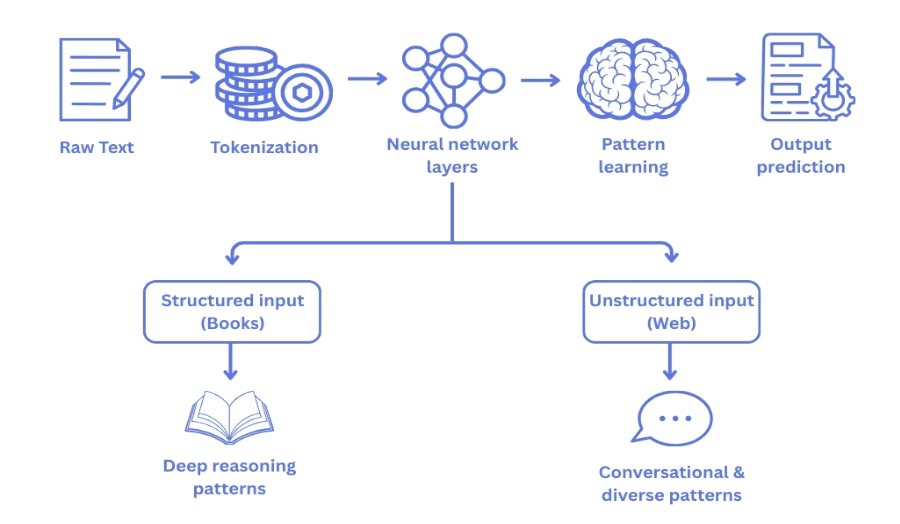
Before we dive deeper, it’s important to understand how LLM models actually learn beneath the hood.At their core, these models don’t“think” or “understand” in the human sense instead; they analyze and internalize patterns from massive volumes of LLM training data. Every sentence, article, book, or code snippet they read is broken down into tokens, the fundamental building blocks of modern AI.The model processes sequentially tokens which represent words subwords symbols, and sometimes even punctuation.
LLM models learn by predicting the next token based on all the previous tokens during training. This simple mechanism allows them to capture extremely complex patterns:
How words connect in meaningful ways
How ideas transition from one sentence to another
How grammar rules hold the structure together
How conversations flow naturally
How logical reasoning is constructed step by step
Over billions of iterations, the model forms an internal “map” of language, reasoning, and context. High-quality training data is crucial for LLM; better patterns result in smarter models and better performance.
Structured vs. Unstructured Data: Why This Difference Matters
The type of data the model is fed has a large influence on this learning process. When it comes to data types, one of the most important distinctions is between structured vs unstructured data.
Structured Data
Structured datasets include sources like:
Books
Academic papers
Encyclopedias
Curated instructional datasets
High-quality manuals or reports
They follow clear grammatical rules, consistent organization, and predictable sentence structures. For LLM models, structured data acts like a well-organized classroom easy to learn from, less noisy, and rich in reliable patterns. This helps models build strong reasoning abilities, coherent long-form responses, and logically sound output.
Unstructured Data
In contrast, unstructured data comes from:
Websites
Social media conversations
Reddit threads
Q&A forums
User-generated content
This data has slang, typos, inconsistent format, emojis, sarcasm, and overall real-world messiness. Although chaotic, unstructured data is vital. It shows LLM models how humans really talk outside of textbooks: casually, emotionally, quickly, and occasionally wrong. It is what makes modern LLM models feel natural and conversational, not robotic.
3. Training LLM Models with Books
3.1 Benefits
Extremely high-quality writing
Books go through a professional editing, structuring, and fact-checking process which makes them far more accurate than web content. This kind of consistency makes sure that LLM models learn from clean, polished language patterns, helping them build stronger linguistic foundations and proving to generate more reliable outputs.
Rich long-form narrative structures
Books provide long stories with chapters, sections, and different ideas connected to each other. Long form text of this sort makes the reasoning and storytelling ability of LLM models robust because it teaches LLM how to develop a theme, stay in context and link information across long text sequences.
Superior grammar and vocabulary
Books use proper grammar and have a rich and varied vocabulary. So, it exposes the LLM models to clean language. As a result, it enhances the ability of the model to output clear and well-structured sentences so that they can become more readable, fluent, and clear. Hence, this is the case for many tasks such as content creation, explanations, and summaries.
Ideal for deep reasoning tasks
Models trained heavily on book-based datasets tend to excel in tasks that require structured thinking, such as explaining concepts, breaking down logical steps, generating detailed analysis, or summarizing complex content. The depth and coherence found in books naturally strengthens a model’s reasoning ability.
3.2 Limitations
Not up to date
It usually takes months or years to publish a book, so the book is rarely up to date with recent events, technology, and culture. This means that when an LLM model relies heavily on books, it loses awareness of more current information compared to models that heavily use the web for their training.
Limited diversity
Although there are a million books, the depth, spread, and variety of the web are far more than that. Books usually have a particular genre, writing style, and perspective in them. So the exposure of LLM models to informal language, new subjects, and a wide variety of viewpoints found online is limited.
Copyright issues
Numerous texts are strictly licensed, meaning other companies cannot use them as training data for their LLMs. Gaining the rights can be costly and complex. This limits the incorporation of robust book data to train large-scale LLM models.
4. Training LLM Models with Web Data
4.1 Benefits
Massive availability
The web is the world’s largest open repository of human-generated text on millions of topics and billions of pages. With this scale, LLM models learn from an incredibly large corpus of material that offers greater variety than even the most carefully curated dataset. The expansive data allows models to learn about many topics.
Real-time information
Web data is timely and reflects the latest trends, events, technologies, and other cultural phenomena like social media. This real-time feature makes LLM models more robust and knowledgeable, allowing them to answer up-to-date questions or respond to rapidly changing subjects that a book or dataset cannot do quickly enough.
Diverse writing styles
The web contains a number of resources – blogs, discussion forums, chat logs, reviews, tutorials, error messages, memes, comments, and many more. Thus, the web is one of the most stylistically diverse data sources available. The different types of articles help train LLM models to pick up varied tones, formal and informal styles, and conversation patterns.
Practical conversational tone
Since the web contains everyday interactions and informal language, it allows the LLM models to sound more human, relatable, and natural. Models that are well-trained on the web tend to be better at dialogue and recognizing slang or shorthand and producing more human-sounding responses.
4.3 Limitations
Misinformation and bias
A major drawback of web data is that it contains false information, biased opinions, manipulated narratives, and unverifiable claims. This requires aggressive cleaning and filtering to prevent these issues from influencing the behavior of LLM models during training.
High compute cost
Because web data is noisy and unstructured, preprocessing takes significantly more time and computational power. Deduplication, classification, quality scoring, filtering, and formatting all add to the compute cost, making large-scale web data processing far more resource-intensive than book datasets.
Inconsistent reasoning quality
Web text rarely reflects structured, logical reasoning. As a result, models trained primarily on web data can develop inconsistent reasoning patterns and are more prone to hallucinations. Without careful balancing with high-quality sources like books or curated datasets, purely web-trained models may generate unreliable or incoherent answers.
5. What Researchers Found: Insights From 2026 Studies
Recent studies and benchmarks from 2026 show:
Models trained heavily on book data score higher on reasoning, explanations, comprehension, and long-context accuracy.
Models trained on more web data score higher on conversation, casual Q&A, pop culture, and everyday context.
Hybrid datasets consistently outperform single-source datasets.
In fact, leading LLM models today include OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Meta, and open-source giants all use blended training pipelines that combine long-form text datasets, book content, filtered web content, and synthetic data.
6. Hybrid Training: The Best of Both Worlds
Training top-tier LLM models today is no longer a simple debate of “books vs. web.” Instead, the modern approach relies on blending both intelligently to build models that are balanced, capable, and adaptable. Hybrid training allows LLM models to combine the structured reasoning strength of books with the vast, real-time diversity of the web. This mix ensures that models can think deeply and communicate naturally, forming the foundation of most state-of-the-art AI systems used today.
Mixture-of-experts architectures
MoE (Mixture-of-Experts) models are designed to route different types of inputs to specialized sub-models that excel in certain domains. For example, a “reasoning expert” might be trained more heavily in books to improve logic and coherence, while a “conversation expert” is trained more on web data to enhance natural dialogue. This specialization improves efficiency, reduces compute cost during inference, and boosts performance across a wide range of tasks.
Example: a “reasoning expert” may be trained more on books, while a “conversation expert” is trained more on web data.
This kind of targeted learning ensures that each expert within the MoE system develops unique strengths. When the model receives a prompt that requires logical depth, the reasoning expert takes over. When the prompt is conversational or informal, the conversational expert responds. This system creates more flexible and intelligent LLM models capable of understanding intent with higher accuracy.
Data curation pipelines
Modern AI teams take advantage of advanced data curation pipelines to score, label, filter, dedup and balance billions of tokens. Only quality training data with no noise, contradictions, and repeated text gets through the above pipelines. It is an important step as if the sources are blended inconsiderately it will hamper the mix and overall model.
Synthetic long-form text generation
Today’s leading LLMs can generate high-quality synthetic data to improve their own reasoning loops. Models create long-form explanations, multi-step reasoning samples, and refined content that can be fed back into training. This synthetic data helps fill gaps in book and web sources, letting models enhance their reasoning abilities without relying exclusively on external text.
Balanced datasets
Instead of chasing sheer scale, companies now prioritize AI training data quality. They choose the best mix of books, web pages, research papers, code, forums, and synthetic text to train versatile LLM models. Balanced datasets allow models to excel in reasoning, conversation, factual accuracy, and creativity all at once.
Hybrid training has become the dominant strategy because it creates LLM models that are more versatile, dependable, and safer than models trained on a single type of data. By combining structure with diversity, hybrid-trained models consistently outperform those trained only books or only web sources.
7. Which Is Better?
The truth is simple: the “better” data source depends entirely on what you want your AI model to achieve. Each type of data provides different strengths, and understanding those strengths helps align the training approach with the intended use case of the LLM model.
For deep reasoning → Books
If your goal is strong logic, detailed explanations, structured summaries, or step-by-step analytical outputs, book-heavy training is superior. The coherence and depth found in books help LLM models form stable reasoning pathways and provide more accurate, structured answers to complex queries.
For real-world knowledge → Web data
Web data is the superior choice when it comes to keeping up with trends, news, and culture. Models that are heavy on web text have a strong informal tone, more conversational styles, and current information. This makes them ideal for interactive assistants, chatbots, and tools that require contemporary relevance.
For overall performance → Hybrid datasets
Balanced datasets get the best scores in benchmarks, evaluations, and real-world performance tests. Using a mix of book depth, web diversity, and reasoning, such hybrid data sets make an LLM model do well in all domains instead of doing well in one domain only.
For safety and accuracy → High-quality curated datasets
In the end, it does not matter where the data comes from but the quality of the AI training data. Datasets that are clean, filtered, high quality, and curated help with hallucination mitigation. This focus on curation helps to make today's LLM models more trustworthy and more aligned.
8. Real-World Use Cases
Here’s how industries choose between book-heavy, web-heavy, or hybrid datasets based on the needs of their LLM models:
Customer service chatbots
These systems typically rely on a blend of web data and curated instruction manuals. Web data gives them natural conversational abilities, helping them understand everyday phrasing, tone, and informal communication. Meanwhile, manuals, FAQs, and documentation ensure the chatbot follows instructions accurately and provides reliable, policy-aligned information.
Medical or legal LLMs
Medical and legal models rely heavily upon book-type databases, peer-reviewed publications, and knowledge-specific long-form text. These areas need accurate reasoning, true knowledge, and careful use of specific concepts. The use of book-heavy data provides satisfactory reliability to ensure that decision-support systems perform well in these applications.
Creative-writing models
Unlike dialogue or task-oriented models, creative-writing models are usually trained with more book-like datasets because they require strong narrative flow, descriptive imagery, stylistic elements, and well-developed story patterns. The steady long-form structure given by books helps these models learn how to replicate authorial devices and generate coherent imaginative outputs.
Social/chat-style AIs
Social AI use web data to learn memes and pop culture references, trendy expressions, and casual conversational flows. Web-centered datasets allow these models to communicate with users in casual contexts while being relatable, expressive, and culturally aware.
Each application requires a different mix of data sources, reinforcing the fact that there is no universal “best” dataset, only the best dataset for a specific purpose.
9. Key Challenges in Using Both Dataset Types
Training modern LLM models with a mix of book and web data introduces several challenges that teams must address through careful dataset engineering and quality control.
Copyright and licensing
Books and many proprietary sources cannot be freely used due to strict copyright restrictions. Acquiring licenses for high-quality text is expensive and complex, which limits the amount of book-based data available for large-scale LLM training.
Data deduplication
Large datasets often have duplicate data or near-duplicates. This is frequently the case with scraped web data. Duplicates that are not removed can obstruct model learning. This can lead to overrepresentation of ideas and inflated token counts. In turn, this can lead to inefficient training.
Conflicting truths
Web material is often contradictory, outdated, or biased. LLM models may sometimes inherit confusion after training on these inconsistencies. They may also provide inappropriate answers unless there are strong filters and verifiers in place.
Scaling compute
Processing a mix of high-quality book data and noisy web data requires enormous compute power. Cleaning pipelines, deduplication, classification, and filtering increase the preprocessing overhead, making hybrid training both resource-intensive and technically challenging.
Bias control
Both web data and books contain some form of bias. While books may distort reading perception due to historical or cultural bias, web images and texts reflect present day bias and distortion. Engineers must create strategies that identify, decrease, and address biases during training.
To manage all these challenges, we need sophisticated dataset engineering, high-end automation, and continual assessment to ensure the LLM models are safe, accurate, and fair.
10. Future of LLM Training Data
As the field evolves, the next generation of LLM models will shift toward smarter and more purpose-driven training data strategies.
More curated, high-quality datasets
The industry is moving away from “bigger is better” and toward “cleaner is better.” Curated datasets where every token is scored, filtered, and validated will become the gold standard for building reliable, high-performance LLM models.
Domain-specific training pipelines
Medical, legal, engineering, finance, robotics and other field-specific models will be trained on specially curated datasets. Each domain terminology, reasoning style, and factual requirements are preserved and optimized at training with these pipelines.
Synthetic long-form datasets
Modern LLMs will increasingly generate their own long-form reasoning and knowledge of samples. This synthetic data helps fill gaps, improves model consistency, and enhances factual grounding especially for complex reasoning tasks.
Smarter filtering systems
Tools that use artificial intelligence will be used to clean huge web datasets. Spam, misinformation, bias, and low-quality text detection systems at scale, ensuring only the best content enters the training pipeline.
Adaptive training approaches
Future LLM models will dynamically adjust the mix of book vs. web data based on real-time performance metrics. If a model shows weakness in reasoning, the pipeline may add more book-heavy data. If it needs better conversational flow, the system may increase web-heavy samples. This makes training more intelligent and outcome driven.
The future of LLM training isn’t about choosing between books and the web it’s about designing the perfect blend that aligns with each model’s mission, strengths, and target use cases.
Summary
This blog explored how LLM models learn and why the debate of book vs web data for AI matters more than ever in 2026. Books offer structure, depth, and superior reasoning, while web data provides diversity, recency, and conversational fluency. The key is balancing both to achieve high AI training data quality using curated, long-form text datasets, structured vs unstructured data in LLMs, and hybrid data pipelines. Modern LLM models rely on high-quality datasets for LLMs, blending strengths from every source to deliver smarter, safer, and more powerful AI systems for real-world applications.


