Prerna Sahni
Feb 9, 2026
LLM
LLM Evaluation Frameworks & Metrics Guide for 2026
1. Introduction
What exactly is the powerhouse we call an LLM model? An LLM model is a revolutionary AI program, pre-trained on a massive, diverse dataset, enabling it to comprehend, generate, and process human-like language. Architecturally, it's a very large deep learning model built on the transformer neural network architecture, employing an encoder and decoder with self-attention capabilities to parallel-process sequences of tokens.
Why does evaluating these complex systems matter so profoundly in 2026? Because as LLM models transition from experimental prototypes to mission-critical enterprise systems handling everything from legal drafting to patient diagnostics, relying on mere "vibes" or a single accuracy score is reckless. A proper evaluation system is the only way to guarantee performance, safety, and compliance at scale.
This guide will aggressively unpack the components of effective evaluation, detail the essential metrics you need to track, and walk you through the most popular LLM evaluation frameworks available today.
2. Why LLM Model Evaluation Matters
Neglecting a comprehensive evaluation strategy is why a staggering number of generative AI projects have been reported to fail. For the technical leader, the stakes are existential:
Performance, Safety, and Reliability: Evaluation improves output quality, reduces the risk of factual inaccuracies (hallucination), and mitigates the generation of harmful or biased content, ensuring the LLM model is genuinely trustworthy.
Impact on Stakeholders: For developers, evaluation ensures reproducible results across iterations. For businesses, it translates technical performance into ROI and reduced risk. For everyday users, it means a reliable, safe, and helpful interaction with the technology.
The Framework Connection: The pressure of modern deployment demands a shift from one-off tests to continuous, multi-dimensional validation. This is why specialized LLM evaluation frameworks are no longer optional; they are central to model selection and AI governance.
3. What Is an LLM Evaluation Framework?
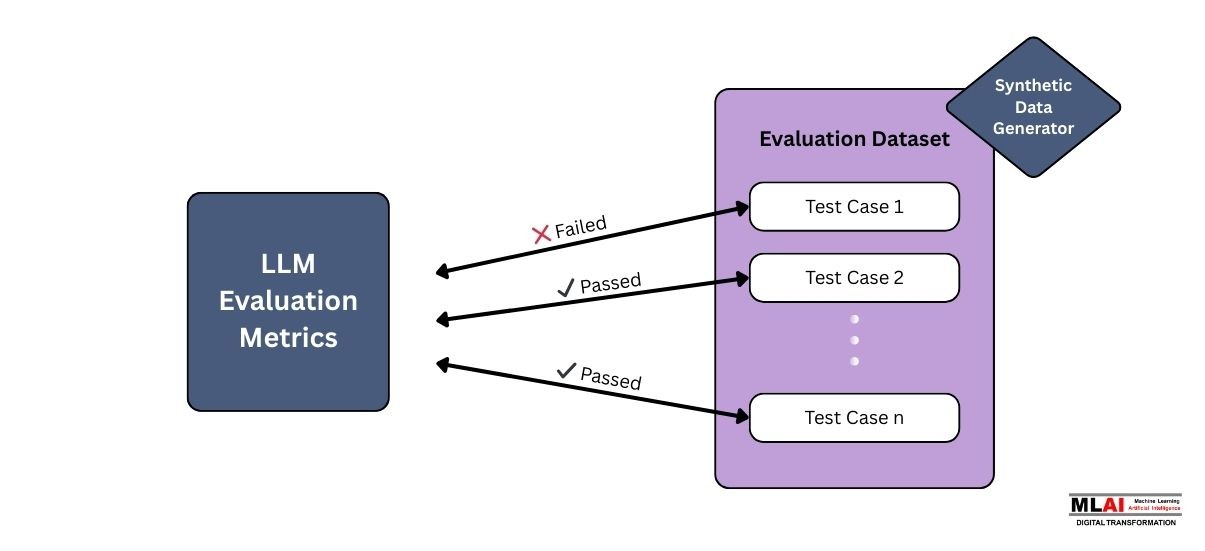
An LLM evaluation framework is simply a structured system used to reliably and repeatedly test how well an LLM model performs the tasks it was designed for, especially against real-world use cases. Think of it as your AI quality control system.
An LLM evaluation framework is a repeatable process combining core technical components:
Framework components: These include datasets, metrics, evaluation pipelines, and scoring mechanisms.
AI model benchmarking: This is the process of comparing your model's performance metrics against competing models or previous versions, giving you a clear, data-driven ranking.
4. Key Components of an Effective LLM Evaluation Framework
To build a robust framework, you need to deliberately structure the testing environment with easy and technical clarity:
Component | Explanation |
Datasets | These include both general datasets (for broad capability testing) and domain-specific/hand-curated "golden" sets to test niche or edge cases, which is crucial for rigorous evaluation. |
Evaluation metrics | These are the quantitative and qualitative scores used to judge the model’s output quality. They include essential measures like accuracy, relevance, and coherence. |
Testing environments | This refers to where the evaluation is run, whether in pre-deployment or utilizing live production monitoring for detecting model drift. |
Human vs automated evaluation | You must utilize automated scoring for fast iteration and scale, and reserve human evaluation for subjective or critical-risk areas like tone, creativity, or ethical alignment. |
Safety, robustness & bias checks | These include specific tests for toxicity detection, measuring bias across demographics, and ensuring prompt injection resilience for security. |
5. Core LLM Performance Metrics
To move beyond the hype, you need a precise toolkit of LLM performance metrics that tell the true story of your LLM model.
5.1 Accuracy Metrics
These measure how "correct" the output is.
Perplexity: Measures how surprised the LLM model is by the test data. A lower score indicates better fluency and prediction of confidence.
Token-level accuracy: Measures the exact match of generated tokens to the ground truth.
Relevance scoring: Measures if the output is pertinent to the user's query.
5.2 Reasoning & Understanding Metrics
These metrics test the model's "intelligence" beyond simple memorization.
Factual consistency: Ensures claims in the response are supported by the source context, which is crucial for grounded systems.
Logical reasoning benchmarks: Standardized tests that require multi-step inference, measuring complex problem-solving abilities.
RAG evaluation: Specific metrics for Retrieval-Augmented Generation evaluation, focusing on Groundedness and Contextual Recall.
5.3 Efficiency Metrics
These are vital for production of readiness and cost control.
Latency: The time-to-first token (TTFT) or total response time, which directly impacts user experience.
Throughput: The volume of tokens the system can process per second, essential for high-volume deployments.
Resource usage: Monitoring of GPU/TPU and memory consumption per request, which is key for cost optimization.
5.4 Safety & Trust Metrics
These ensure ethical deployment and risk mitigation.
Toxicity detection: Identifying and quantifying harmful, profane, or abusive outputs.
Bias measurement: Quantifying fairness across different protected demographic groups.
Hallucination rate: The percentage of responses containing factually incorrect information not present in the source context.
6. Popular LLM Evaluation Frameworks in 2026
Choosing the right tool dramatically accelerates your evaluation pipeline. Here are five powerful, widely adopted LLM evaluation frameworks, provided with a mix of beginner and technical details:
HELM (Holistic Evaluation of Language Models):
This is a living, reproducible benchmark that evaluates models across a massive, diverse matrix of tasks and scenarios. It uses metrics like accuracy, calibration, efficiency, and fairness, making it suitable for strategic model selection and broad comparison of foundational LLM models.
LM Eval Harness:
This is a python library to provide standardized evaluation of a number of tasks (MMLU, HellaSwag). The method focuses on accuracy for a specific task and zero/few-shot performance which allows benchmarking of AI models quickly in a standardized manner and for model-to-model comparisons.
OpenAI Evals:
A framework that commonly employs an LLM model (typically, some variant of GPT) as a judge for scoring outputs, often through elaborate chain-of-thought prompting. It measures subjective quality (helpfulness, tone) and factual consistency, suitable for evaluating open-ended generation and chat systems.
LangChain Evaluation Toolkit:
Integrated tools for evaluating entire application pipelines (like RAG chains), not just the base model. The use of latency checks and RAG specific metrics (Faithfulness, Answer Relevance) is essential for real-world evaluation of complex multi-step LLM applications.
RAG-based Evaluation Tools:
Specialized frameworks focused on the unique issues dealt with Retrieval-Augmented Generation with measures such as context precision and groundedness. This is important for applications that depend on external knowledge bases.
7. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Evaluate an LLM Model in 2026
This is your actionable roadmap for rigorous, business-aligned testing:
Step 1: Define objectives (accuracy, safety, speed): Translate high-level business goals into specific, measurable technical targets.
Step 2: Choose a benchmarking dataset: Select or create a dataset that exactly mirrors your real-world production inputs.
Step 3: Select relevant metrics: Define a tight, focused set of 3-5 LLM performance metrics based on your objectives.
Step 4: Run automated tests: Implement your chosen LLM evaluation framework to run your model against the dataset and generate initial scores automatically.
Step 5: Human evaluation (optional but important): Send a sampled subset of outputs to domain experts for qualitative review on subjective qualities like tone or ethical alignment.
Step 6: Compare results using AI model benchmarking: Systematically compare the results against a baseline (competitor or previous version) to measure genuine progress.
Step 7: Optimize & retest: Use the identified failure modes to fine-tune the model or refine the prompt template, then run the entire process again to validate the fix.
8. Technical Deep Dive: Modern Benchmarking Techniques
For the advanced ML engineers, classic metrics are just the starting point. These modern techniques unlock a deeper understanding of your LLM model's capabilities:
Prompt-based evaluation: Using prompts designed to elicit a particular behaviour from the model e.g. asking the model to “explain its reasoning step-by-step”.
Embedding similarity scoring: Using vector embeddings (such as cosine similarity), we can measure how semantically-close the generated output is to the ground truth and not just word overlap.
Chain-of-thought evaluation: Testing a model's ability to logically reason by observing the intermediate steps it takes to reach a solution.
Scenario simulation frameworks: Creating difficult dialogue situations over multiple turns to test coherence and planning in the long run.
Using synthetic datasets for stress testing: Creating large quantities of synthetic, structured prompts to quickly discover rare failure modes and force model limits.
9. Real-World Examples: Evaluating LLM Models in Different Industries
The critical LLM performance metrics shift based on the deployment context, using simple use cases:
Healthcare: The critical focus is on factual accuracy & safety. Evaluation must include tests against medical guidelines with a zero-tolerance policy for hallucination in diagnostic summaries.
Finance: Compliance and hallucination checks are paramount. Evaluation involves creating a "compliance guardrail" check to verify that all generated text adheres to regulatory standards.
E-commerce: The focus is on relevance & personalization. The evaluation must measure how well the LLM model generates highly relevant product descriptions or customer service responses.
Education: Reasoning & clarity are key. Testing includes logical reasoning benchmarks and qualitative human review to ensure explanations are coherent and technically correct.
10. Challenges in LLM Model Evaluation (And How to Overcome Them)
The road to an elite LLM model is paved with evaluation challenges:
Constant model updates: The underlying model can be updated silently, causing sudden performance shifts (drift). Solution: Implement real-time LLM monitoring on production data samples.
Lack of universal benchmarks: Public benchmarks don't reflect your unique business use case. Solution: Invest in creating a small, high-quality, hand-curated "golden dataset" of critical prompts.
Bias and fairness issues: Automated metrics often miss subtle biases. Solution: Use adversarial testing with inputs designed to elicit biased responses and incorporate human review.
Context length differences: Variability in models' maximum context windows can impact results. Solution: Standardize your test prompts to a uniform length relevant to your application's needs.
Measuring reasoning vs memorization: A model might pass a test by memorizing the training data. Solution: Use novel, synthetic test cases that require inference and generalization.
11. Future Trends in LLM Evaluation for 2026 and Beyond
The future of evaluation is moving toward full automation and self-correction:
Automated evaluation agents: Specialized AI agents that actively run multi-step testing scenarios, simulating complex user behavior.
Real-time LLM monitoring: Evaluation moving directly into the production pipeline, continuously checking live traffic for errors and violations.
Multimodal benchmarking: New frameworks to simultaneously test coherence, safety, and factual accuracy across different data types (text, image, audio).
Self-evaluating LLMs: Models engineered to score their own outputs based on a set of internal criteria, allowing for real-time internal feedback.
Conclusion
In 2026, LLM models revolutionise industries' evaluation of the models must be more severe and therefore multifaceted evaluations are urgent. An ecosystem for Artificial Intelligence at this point cannot be built on guesswork, superficial metrics, or antiquated benchmarks. What is required instead is a well-defined evaluation strategy that involves solid LLM evaluations, specific LLM measurement metrics, and consistent benchmarking of the AI model.
By understanding core components, applying advanced testing techniques, and integrating real-world evaluation practices, organizations can confidently deploy LLM models that are safer, smarter, and enterprise ready. Ultimately, the quality of an AI system is defined not just by its capabilities but by how well it is evaluated. Let thoughtful evaluation be your competitive advantage.


